McKinsey & Company has released a new analysis predicting a significant shift from traditional and institutional care models to home healthcare within the next three years. Here, we provide a summary of their findings, including the reasons behind this anticipated shift, the impact to services, factors influencing adoption and how home healthcare providers can encourage growth.
Key Findings
McKinsey & Company based their findings on survey results collected from healthcare providers serving both Medicare fee-for-service (FFS) and Medicare Advantage (MA) patients. Based on the survey responses, the authors predicted that 25% of total services will shift from facilities to community-based care by 2025, which totals a value of approximately $225 billion.
If accurate, this would increase the amount of services provided at home three to four times the current average. Yet, this increase to HCBS, predicted to occur by 2025, would not create a reduction in quality of access. Instead, the authors predicted quality of care and patient experience would be improved.
Reasons For The Shift
The primary reason for this anticipated transition to HCBS has been the COVID-19 pandemic. Multiple factors have contributed to a change in thinking around home healthcare and also to practical considerations for HCBS. Those noted by the authors included:
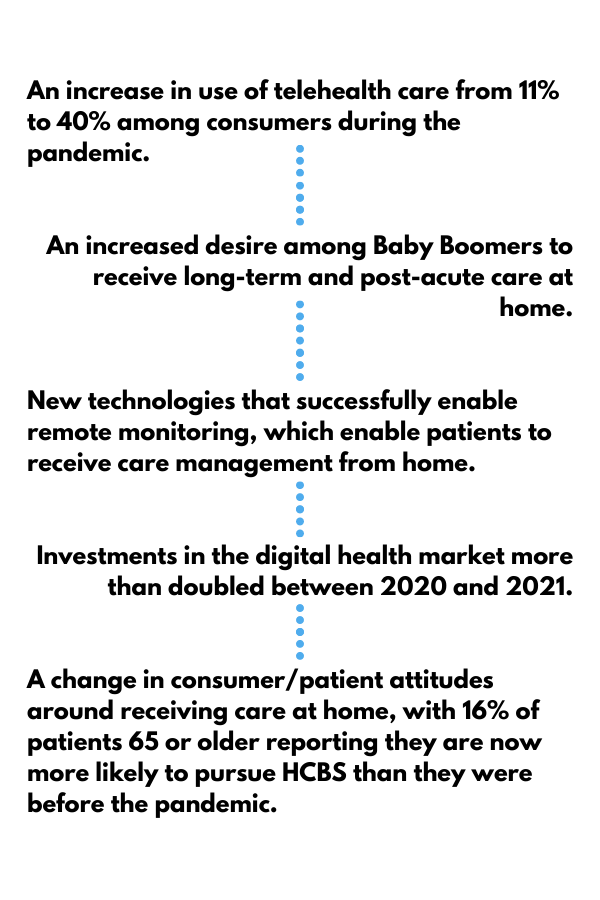
Impact To Services
Using the survey results, the authors identified and categorized services that could be performed at home, rather than a facility, clinic or doctor’s office. This breaks down as follows:
- Services already in place that are scalable. This represents 15% to 40% of Medicaid FFS and MA spending, and includes:
- Primary care
- Out-patient consults
- Urgent care or ER visits
- Out-patient mental health and behavioral health treatment
- Services that could potentially be moved to the home by combining existing offerings. This represents 15% to 40% of Medicaid FFS and MA spending, and includes:
- Dialysis
- Post-acute care
- Long-term care
- Services that could be further developed. This represents 20% to 30% of Medicaid FFS and MA spending, and includes:
- Acute care
- Some chronic conditions
Factors Influencing Adoption
The future success and growth of HCBS depends heavily on adoption, support and buy-in from multiple stakeholders, such as physicians, patients, investors and technology companies.
Economic viability is also a critical factor. Changes to reimbursement policies or new innovations in payment arrangements—such as payment parity or value-based payments—would help incentivize adoption.
Patient perception is the final factor identified by the authors. A positive perception, combined with increased awareness of how to access and use services, could strongly influence growth.
Encouraging HCBS Growth
For providers of HCBS, collaborating with others and looking for strong partnerships remains a vital strategy in maintaining strength and flexibility in the home healthcare industry. The authors noted collaboration with investors and technology companies will be most useful for encouraging growth:
- Primary health telecare, dialysis provided in-home and remote monitoring all represent opportunities for expansion within the industry that investors may see as a strong business opportunity.
- Partnering with technology companies may enable providers to create, buy, or mutually benefit from new tech solutions, which ultimately contributes to the number of solutions available to those looking to expand their home-health offerings.
Learn more about our partnership process, and be sure to check out our Topics of Impact series for insider insights into HCBS.

